LOG IN. UPLOAD PICTURES.
The Philippines has Zambo Mart to help propagate the Chavacano Language.
Akrotiri
 Location of Akrotiri within the continent of Europe | |||
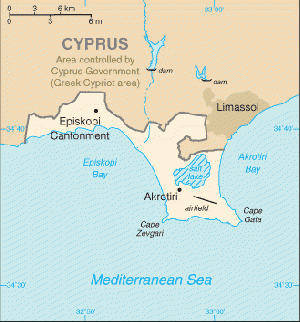 Map of Akrotiri | |||
 Description of Flag: Akrotiri flies the flag of the Unied Kingdom | |||
|
Background of Akrotiri
The Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia are two British-administered areas comprising a British Overseas Territory on the island of Cyprus administered as Sovereign Base Areas of the United Kingdom. The bases were retained by the British following the granting of independence and the eventual transition of Cyprus from a crown colony to an independent sovereign state.
Demographics of Akrotiri
History of Akrotiri
Akrotiri was first constructed in the mid-1950s to relieve pressure on the main RAF station on the island, RAF Nicosia. In the aftermath of the Egyptian repudiation of the Anglo-Egyptian treaty, British forces had to be withdrawn from the Canal Zone in Egypt. After the ending of the League of Nations mandate over Palestine in 1948, the only other British territory in the eastern Mediterranean was Cyprus. Consequently, the withdrawal from Egypt caused an enormous build-up of forces in Cyprus. This period also coincided with the outbreak of the internal security problems of EOKA in Cyprus, further increasing pressure on the RAF airfields on the island.
Even this massive influx from Egypt was not the end. In late 1956, relations between the United Kingdom and Egypt had reached crisis point. The Suez Crisis saw a further increase in the strength of RAF forces in Cyprus. Akrotiri was mainly an airfield for fighter, photo reconnaissance and ground attack aircraft. Its regular squadrons of Meteor night fighters, Canberra photo reconnaissance aircraft and Venom ground attack machines were reinforced by further Canberras and Hunters from Fighter Command in the United Kingdom. The airfields in Cyprus were so overcrowded that there was a real fear of massive loss of equipment should the Egyptian Air Force decide to attack the island. Fortunately for the RAF, that attack never came. The overcrowding extended beyond Cyprus. Significant RAF units from Bomber Command were deployed to RAF Luqa in Malta, crowding that station as well.The attack on Egypt was a military success, despite interference in the plan which reduced its effectiveness. However, it was a political fiasco, because the United States put considerable pressure on the United Kingdom and France both economically and politically. This quickly forced the Eden government from power. The quickness of the climbdown was good news for the personnel at Akrotiri. The station's complement quickly returned to normal after the crisis passed, with the reinforcing units that had crowded it during the war returning either to the United Kingdom or to other parts of the Middle East Command.
After the Suez Crisis, the main emphasis of life on the airfield shifted to helping quell the EOKA revolt and training missions. After the withdrawal from both Egypt and Iraq, and débâcle of Suez, it was clear that a command centred on Cyprus could not control units stationed in the Arabian Peninsula, of which there were still many. Consequently, the Middle East Command was split, with that east of Suez being controlled from Aden, and the rump being renamed the Near East Command, controlled from Cyprus. From 1957 to 1969, four squadrons of Canberras (Nos 6, 32, 73, and 249) provided first a conventional and then from November 1961, a nuclear striking capability as part of the Baghdad Pact, later CENTO.[2]
Akrotiri, along with Nicosia, assumed a very important status, as virtually the sole means for projecting British airpower into the eastern Mediterranean, outside of aircraft carriers. In 1960, independence was granted to Cyprus, with the RAF maintaining both RAF Nicosia and RAF Akrotiri as airfields, controlled by the Near East Air Force. However, Akrotiri assumed more and more importance as Nicosia was used for greater and greater amounts of civil aviation traffic. After 1966, it was no longer possible to maintain RAF units at Nicosia due to pressures of space, and Akrotiri became the only RAF flying station left on the island.
In August 1970 a detachment of "G" of the Central Intelligence Agency arrived at the airfield with U-2 aircraft to monitor the Egypt/Israel Suez Canal fighting and cease fire. Later permanent monitoring of Middle East Ceasefire after 1973 Yom Kippur War. It became the 100th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing OL "Olive Harvest" in 1974.[3]
Up until 1974 RAF Akrotiri had a balanced force of aircraft assigned to it, including No. 9 Squadron RAF and No. 35 Squadron RAF flying Vulcans. The Vulcans provided a bomber force for the Central Treaty Organisation, one of the three great anti-Communist mutual defence pacts signed in the early days of the Cold War.[4] However, during that year, Turkish forces invaded Cyprus in connection with a Greek-sponsored coup. The UK then evacuated most of the RAF from Akrotiri as the CENTO treaty had degenerated to the point of uselessness. The two Vulcan squadrons left for UK stations in 1975. What was left at the airfield was the flying unit that is permanently assigned to the station to this day; No. 84 Squadron RAF, a search and rescue unit flying helicopters.[5] In addition the role of No. 34 Squadron RAF Regiment was changed from Low level Air Defence to infantry and counter terrorist duties.
In September 1976 the US U-2 operations were turned over to the 9th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing, but the U-2 operation at RAF Akrotiri continued to be called Operating Location OH until September 1980. Thereafter it became Detachment 3 of the 9th SRW, although the name OLIVE HARVEST continues. Two U-2s are stationed at RAF Akrotiri and they are still monitoring the ceasefire agreement between the Egypt and Israel although the present operations in Central Command requires further missions. U-2s also transit through RAF Akrotiri either on going into the Central Command theatre or returning to Beale AFB.
In the mid-1980s, the US launched retaliatory attacks against Libya after the country's leader, Muammar al-Gaddafi, was implicated in terrorist attacks against US military bases. Although the bombers were staged out of the United Kingdom, RAF Akrotiri was employed in the role of an alternate in case of emergency, and was used as such by at least one aircraft. This caused a severe upgrade in security around the airfield as Libya threatened to respond against locations used in staging the attacks. The threat was carried through with an attack on the station on 3 August 1986 with mortars, rocket-propelled grenades and small arms. Three British dependants were wounded although damage was negligible. Security at the station remained high with substantial fortifications constructed along its northern perimeter, until the first Gulf War. The attack was carried out by an unknown supposed Palestinian group but it was generally assumed that this was commissioned and underwritten by Libya.
Geography of Akrotiri
- Location : Eastern Mediterranean, peninsula on the southwest coast of Cyprus
- Geographic coordinates: 34 37 N, 32 58 E
- Map references: Middle East
- Area: total: 123 sq km, note: includes a salt lake and wetlands
- Area - comparative: about 0.7 times the size of Washington, DC
- Land boundaries: total: 48 km, border countries: Cyprus 48 km, Coastline 56.3 km
- Climate: temperate; Mediterranean with hot, dry summers and cool winters
- Environment - current issues: hunting around the salt lake; note - breeding place for loggerhead and green turtles; only remaining colony of griffon vultures is on the base
- Geography - note: British extraterritorial rights also extended to several small off-post sites scattered across Cyprus; of the Sovereign Base Area (SBA) land, 60% is privately owned and farmed, 20% is owned by the Ministry of Defense, and 20% is SBA Crown land
- Akrotiri and Dhekelia cover 3% of the land area of Cyprus, a total of 254 km2 (98 sq mi) (split 123 km2 (47 sq mi) (48.5%) at Akrotiri and 131 km2 (51 sq mi) (51.5%) at Dhekelia). 60% of the land is privately owned as freeholds by Cypriot citizens; the other 40% is controlled by the Ministry of Defence as Crown lease hold land.[24][25] In January 2014, an agreement between the Cypriot government and the UK one was signed, ensuring that residents and property owners in the British Bases will enjoy equal rights for the development of property.[26] In addition to Akrotiri and Dhekelia, the Treaty of Establishment also provided for the continued use by the British Ministry of Defence and the British Armed Forces of certain facilities within the Republic of Cyprus, known as Retained Sites.
Akrotiri is located in the south of the island, near the city of Limassol (or Lemesos). Dhekelia is in the southeast, near Larnaca. Both of these areas include military bases, as well as farmland and some residential land. Akrotiri is surrounded by territory controlled by the Republic of Cyprus, but Dhekelia also borders on the United Nations (UN) buffer zone and the area controlled by the Turkish forces.
Ayia Napa lies to the east of Dhekelia. The villages of Xylotymbou and Ormidhia, also in the Republic of Cyprus, are enclaves surrounded by Dhekelia. The Dhekelia Power Station, divided by a British road into two parts, also belongs to Cyprus. The northern part is an enclave, like the two villages, whereas the southern part is located by the sea, and therefore not an enclave, though it has no territorial waters of its own.
Territorial waters of 3 nautical miles (5.556 km) are claimed, and the right according to the laws of the United Nations to extend the claim of up to 12 nautical miles (22.224 km) is reserved.[27]
Demographics of Akrotiri
- Population: approximately 15,700 live on the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia including 7,700 Cypriots, 3,600 Service and UK-based contract personnel, and 4,400 dependents
- Languages: English, Greek
Akrotiri and Dhekelia cover 3% of the land area of Cyprus, a total of 254 km2 (98 sq mi) (split 123 km2 (47 sq mi) (48.5%) at Akrotiri and 131 km2 (51 sq mi) (51.5%) at Dhekelia). 60% of the land is privately owned as freeholds by Cypriot citizens; the other 40% is controlled by the Ministry of Defence as Crown lease hold land.[24][25] In January 2014, an agreement between the Cypriot government and the UK one was signed, ensuring that residents and property owners in the British Bases will enjoy equal rights for the development of property.[26] In addition to Akrotiri and Dhekelia, the Treaty of Establishment also provided for the continued use by the British Ministry of Defence and the British Armed Forces of certain facilities within the Republic of Cyprus, known as Retained Sites.
Akrotiri is located in the south of the island, near the city of Limassol (or Lemesos). Dhekelia is in the southeast, near Larnaca. Both of these areas include military bases, as well as farmland and some residential land. Akrotiri is surrounded by territory controlled by the Republic of Cyprus, but Dhekelia also borders on the United Nations (UN) buffer zone and the area controlled by the Turkish forces.
Ayia Napa lies to the east of Dhekelia. The villages of Xylotymbou and Ormidhia, also in the Republic of Cyprus, are enclaves surrounded by Dhekelia. The Dhekelia Power Station, divided by a British road into two parts, also belongs to Cyprus. The northern part is an enclave, like the two villages, whereas the southern part is located by the sea, and therefore not an enclave, though it has no territorial waters of its own.
Territorial waters of 3 nautical miles (5.556 km) are claimed, and the right according to the laws of the United Nations to extend the claim of up to 12 nautical miles (22.224 km) is reserved.[27]
Government of Akrotiri
- Country name: conventional long form: none
- conventional short form: Akrotiri
- Dependency status: a special form of UK overseas territory; administered by an administrator who is also the Commander, British Forces Cyprus
- Capital
- name: Episkopi Cantonment (base administrative center for Akrotiri and Dhekelia)
- geographic coordinates: 34 40 N, 32 51 E, time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
- daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
- Affiliation :(UK Sovereign Base Area)
- Constitution :presented 3 August 1960, effective 16 August 1960; amended 1966 (The Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia Order in Council 1960, serves as a basic legal document) (2013)
- Legal system: laws applicable to the Cypriot population are, as far as possible, the same as the laws of the Republic of Cyprus; note - the Sovereign Base Area Administration has its own court system to deal with civil and criminal matters
- Executive branch
- chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952)
- head of government: Administrator Major General Richard CRIPWELL (since January 2013); note - reports to the British Ministry of Defense; the Chief Officer is responsible for the day-to-day running of the civil government of the Sovereign Bases
- elections: none; the monarchy is hereditary; the administrator appointed by the monarch
- Judicial branch: \
- highest court(s): Senior Judges' Court (consists of several visiting judges from England and Wales)
- judge selection and term of office: judges appointment and tenure NA
- subordinate courts: Resident Judges' Court; Courts Martial
- Diplomatic representation in the US
- none (overseas territory of the UK)
- Diplomatic representation from the US: none (overseas territory of the UK)
- Flag description: the flag of the UK is used
- National anthem: note: as a United Kingdom area of special sovereignty, "God Save the Queen" is official (see United Kingdom)
Economy of Akrotiri
- Economy - overview: Economic activity is limited to providing services to the military and their families located in Akrotiri. All food and manufactured goods must be imported.
- Exchange rates: note: uses the euro
Telecommunication of Akrotiri
- Broadcast media: British Forces Broadcast Service (BFBS) provides multi-channel satellite TV service as well as BFBS radio broadcasts to the Akrotiri Sovereign Base (2009)
Military Profile of Akrotiri as of 2014
- Military - note defense is the responsibility of the UK; Akrotiri has a full RAF base, headquarters for British Forces Cyprus, and Episkopi Support Unit
Population of Akrotiri
- Population: no indigenous inhabitants
note: approximately 1,300 military personnel are on the base; there are another 5,000 British citizens who are families of military personnel or civilian staff on both Akrotiri and Dhekelia; Cyprus citizens work on the base, but do not live there
Disclaimer
This is not the official site of this country. Most of the information in this site were taken from the U.S. Department of State, The Central Intelligence Agency, The United Nations, [1],[2], [3], [4], [5],[6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14],[15], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23], [24],[25], [26], [27], [28], [29], [30],[31], [32], [33], [34], and the [35].
Other sources of information will be mentioned as they are posted.